All Categories
Featured
Table of Contents

Communicate these concerns to pertinent project groups, adhere to via till there's a solution, and report the customer resolution. Make certain that all jobs are following their budgets and shipment times. Make a behavior of tracking job milestones and dependencies. Include these things in your routine records. Team up with other pertinent departments, including the product, sales, and support divisions.
Create a system to strategy, track, and document every solitary program you manage. At least 4-6 years of experience in program management with IT tasks is vital.
Advancement is the name of the video game when it pertains to the innovation industry, and within that standard, there's a behind-the-scenes orchestrator making sure whatever runs seamlesslythe Technical Program Supervisor (TPM). This unrecognized hero plays a crucial duty in the success of tech projects, bringing order to mayhem and ensuring that the gears of development turn smoothly.
Technical Program Manager Salary
It's a fragile dance in between setting ambitious goals and guaranteeing assumptions stay strongly based in truth - top technical program manager jobs. technical program management. However it's not practically developing a strategy; it has to do with performing it perfectly. TPMs wear the hats of both visionary coordinators and practical executors, making sure that every action aligns with the overarching project purposes
In the vast landscape of tech jobs, reliable interaction is the bridge that links diverse teams and stakeholders. Right here, TPMs radiate as proficient translators, deciphering the elaborate language of technology for non-technical stakeholders. They link the gap, making certain that everyone, regardless of their technological history, comprehends the job's objectives and progress.
They possess the insight to recognize potential mistakes, ranging from unforeseen technical challenges to outside factors beyond the team's control. TPMs develop techniques to reduce dangers, making certain that the task cruises through stormy weather condition with strength.
Right here, TPMs take on the function of allocators-in-chief, strategically distributing sources to enhance efficiency. As the project landscape shifts, TPMs reapportion resources dynamically, making certain that the group remains agile and receptive.
How do I master the skills of a Program Manager Vs Technical Project Manager?
TPMs, in this regard, end up being the gatekeepers of quality. They established stringent standards for every element of the job, from code to layout, making certain that the end product meets or goes beyond the defined criteria.
TPMs create a culture where quality is not simply an objective but a behavior, penetrating every facet of the project. Through their precise oversight, they instill self-confidence in stakeholders and add to the long-term success and credibility of the organization. Being an effective TPM calls for greater than simply a propensity for project management.
What makes a good Microsoft Technical Program Manager Interview resume?
While TPMs may not be coding wizards, they need a strong understanding of the technical landscape. This consists of experience with the modern technologies involved, an awareness of market trends, and the capability to understand the ramifications of technical choices.
TPMs are the interaction nexus of a project. Whether it's sharing intricate technological information to a non-technical audience or promoting cooperation amongst team participants, effective interaction is non-negotiable.
Strategic assuming includes preparing for difficulties, visualizing the job's trajectory, and aligning it with wider organizational goals. As modern technology evolves, so does the duty of the TPM. In recent times, the landscape has actually seen a shift in emphasis from standard project management to a much more dynamic and adaptive approach. Agile has actually come to be greater than just a buzzword; it's a lifestyle for several TPMs.
, has become a foundation in the TPM's toolkit. In the age of large information, TPMs are significantly depending on data-driven understandings to inform their decision-making processes.
Best Tpm Courses

Unlike standard task managers, TPMs must deeply comprehend the technological elements of the tasks they manage. This double expertise enables them to interact with design groups properly, understand technical obstacles, and guarantee that projects are finished in a timely manner and within spending plan. Whether you're wanting to hire a TPM or become one, understanding the responsibilities and skill sets needed is important for success in the tech market.
The courses cover important subjects such as task lifecycle monitoring, threat analysis, source allowance, and software advancement procedures. With a concentrate on real-world applications, our training guarantees you are prepared to deal with the complexities of technical jobs in any type of sector. Making a qualification can significantly enhance your career prospects, showing to companies that you possess the expertise and skills needed to prosper in a TPM function.
From start-ups to Lot of money 500 business, companies around the world are seeking qualified professionals to lead their technological programs. Whether you're aiming to hire a TPM or are interested in TPM jobs, TPM Institute can aid you navigate the work market and attach you with the right possibilities. Our courses are not nearly finding out; they have to do with releasing your job in among the most in-demand areas in the technology sector.
Our are committed to giving you with the very best feasible education, supplying insights grounded in real-world experience. They are dedicated to helping you accomplish your certification and be successful in your job. For more details regarding our programs and accreditations, at Take the next action in your career with TPM Institute and become a leader in technological program monitoring.
How do I get certified as a Amazon Tpm Interview Process?
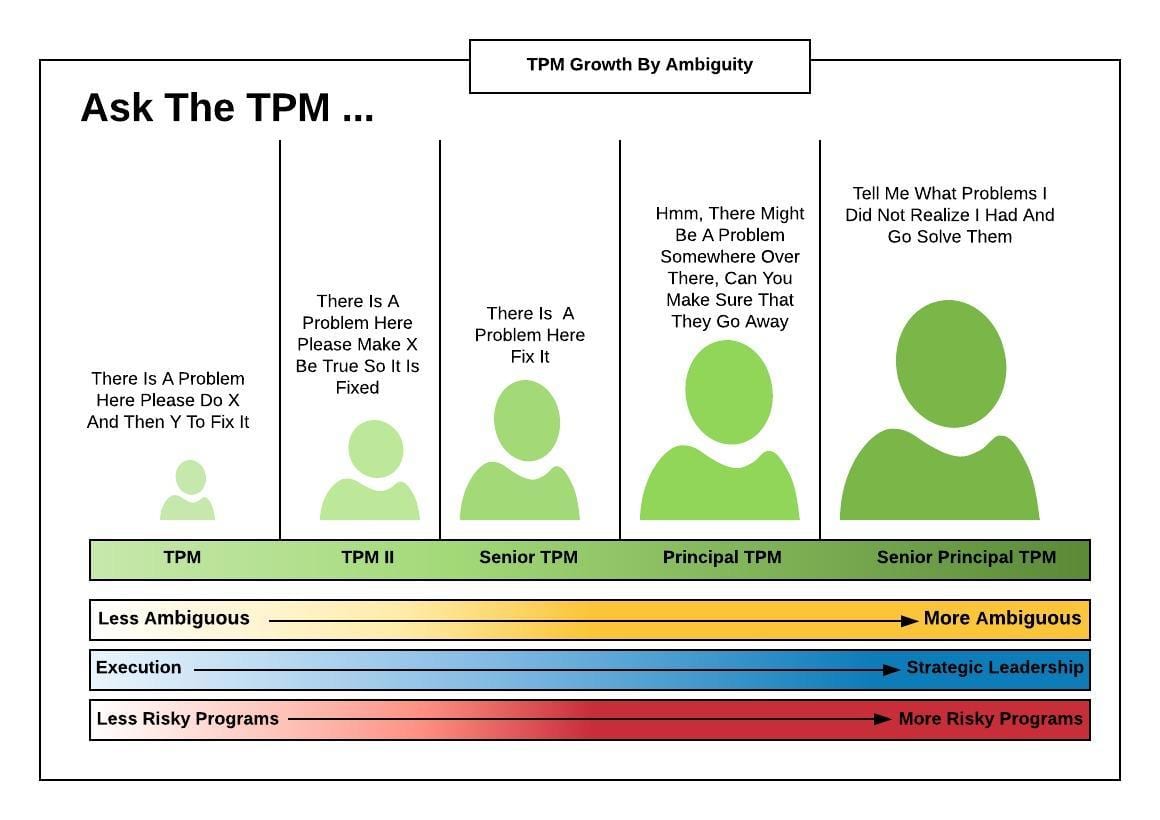
There's a propensity for folks to gravitate towards extremes when conceptualizing technical program managers. They're often explained as either constantly taking part in coding or not at all. The truth exists is a spectrum of technical deepness among TPMs, and this frequently differs by job and customer. Some tasks require a leader with just adequate technological deepness to recognize technology design and trade-offs.
They can express intricate technical concepts to non-technical stakeholders and assist in cooperation between varied teams. TPMs succeed at recognizing and settling issues that arise throughout job execution, making sure that tasks stay on routine and within spending plan.
TPMs work to ensure that all staff member are working towards the same purposes, protecting against miscommunication and thrown away effort. They anticipate and adjust to adjustments in job needs, guaranteeing that tasks can pivot smoothly when needed. TPMs proactively address prospective concerns, minimizing the chance of job delays and failings. They urge their groups to try out originalities and modern technologies, driving continuous enhancement and growth.
TPMs function to guarantee that all group participants are working towards the exact same objectives, preventing miscommunication and lost effort. TPMs proactively deal with prospective problems, decreasing the chance of task hold-ups and failings.
Table of Contents
Latest Posts
The Best Courses For Machine Learning Interview Preparation
10 Proven Strategies To Ace Your Next Software Engineering Interview
Most Common Data Science Interview Questions & How To Answer Them
More
Latest Posts
The Best Courses For Machine Learning Interview Preparation
10 Proven Strategies To Ace Your Next Software Engineering Interview
Most Common Data Science Interview Questions & How To Answer Them